Abstract
Research Article
Molecular analysis of immunoglobulins related to Salmonella typhi in pediatric patients
Farah Qudsia, Muhammad Rehan and Samreen Riaz*
Published: 24 April, 2020 | Volume 4 - Issue 1 | Pages: 005-010
Typhoid fever is a systemic infection caused by Salmonella enterica serotype typhi. It is of major concern in tropical regions of the world. Highest episodes of typhoid fever occur in Asia i.e.93%. Early diagnosis of the disease is mandatory to lower the mortality rate associated with it as well as to prevent the emergence of antimicrobial drug resistance by Salmonella typhi. Research work was conducted in Immunology Department of the Children’s Hospital, Lahore for the period of one year including a total of 60 patients suspected of having typhoid fever. Serum samples of these patients were tested for typhidot IgG and IgM antibodies as well as for the antibodies against TO and TH antigens using Widal test. Of the total 60 patients, 10 (16.7%) were positive for both typhidot IgG and IgM, 16 (26.7%) were positive for typhidot IgM, 3 (5%) were Positive for typhidot IgG and 31 (51.66%) were negative for both typhidot IgG and IgM. Reading the results of Widal test, 8 (13.33%) were positive for Widal TO and TH antigens, 3 (5%) were positive for Widal TO antigen, 19 (31.7%) were positive for Widal TH antigen and 30 (50%) were negative for Widal TO and TH antigens. IgM is positive at the early stage of acute typhoid fever, IgM along with IgG positive means the middle stage of acute illness. The detection of only IgG cannot discriminate between acute and convalescent phases as it can stay in the serum for at least 2 years or more. The typhidot test is much helpful for the rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever as compared to Widal test which is still being used in some set ups in poor countries, although has become mostly obsolete. By testing the rise of IgM and IgG antibodies against Salmonella typhi, we can detect the infection at early and late stages, respectively
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001017 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Febril illness; typhidot; Widal; Immunoglobulin G; Immunoglobulin M
References
- Crump JA, Sjölund KM, Gordon MA, Parry CM. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, laboratory diagnosis, antimicrobial resistance, and antimicrobial management of invasive Salmonella infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015; 28: 901-937. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26180063
- De Jong HK, Achouiti A, Koh GC, Parry CM, et al. Expression and function of S100A8/A9 (calprotectin) in human typhoid fever and the murine Salmonella model. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015; 9: e0003663. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25860480
- Typhoid: Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals. 2015.
- Steele AD, Hay Burgess DC, Diaz Z, Carey ME, Zaidi AK. Challenges and opportunities for typhoid fever control: a call for coordinated action. Clini Infect Dis. 2016; 62: S4-S8. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26933019
- Ayub U, Khattak AA, Saleem A, Javed F, Siddiqui N, et al. Incidence of typhoid fever in Islamabad, Pakistan. Am-Eurasian J Toxicol Sci. 2015; 7: 220-223.
- Akullian A, Ng’eno E, Matheson AI, Cosmas L, Macharia D, et al. Environmental transmission of typhoid fever in an urban slum. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015; 9: e0004212. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26633656
- Mehmood K, Sundus A, Naqvi IH, Ibrahim MF, Siddique O, et al. typhidot-A blessing or a menace. Pak J Med Sci. 2015; 31: 439-443. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26101507
- Kumar KS, Suganya M, Sathyamurthi B, Anandan H. Reliability of typhidot Rapid Immunoglobulin M and Immunoglobulin G in the diagnosis of Typhoid fever. Int J Sci Study. 2016; 4: 256-259.
- Khan MN, Shafee M, Hussain K, Samad A, Awan MA, et al. Typhoid fever in paediatric patients in Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan. Pak J Med Sci. 2013; 29: 929-932. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24353661
- Prasad K, Oberoi J, Goel N, Wattal C. Comparative evaluation of two rapid Salmonella-IgM tests and blood culture in the diagnosis of enteric fever. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2015; 33: 237-242. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25865974/
- Krishna S, Desai S, Anjana V, Paranthaaman R. typhidot (IgM) as a reliable and rapid diagnostic test for typhoid fever. Annals Tropi Med Public Health. 2011; 4: 42.
- Muthaiyan J, Moomin MRA, Varadarajan P, Jayachandran G. A comparative study of typhidot test and Widal test with the culture-positive typhoid fever in children. Cough. 2016; 15: 57.
- Keddy KH, Sooka A, Letsoalo ME, Hoyland G, Chaignat CL, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of typhoid fever rapid antibody tests for laboratory diagnosis at two sub-Saharan African sites. Bull World Health Organ. 2011; 89: 640-647. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21897484
- Jindal N, Bansal R, Grover P, Malhotra R, Singh S. Rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever–a comparative study of typhidot and widal test. Int J Bioassays. 2014; 3: 3438-3440.
- Mitra R, Kumar N, Trigunayat A, Bhan S. New advances in the rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever. African J Microbiol Res. 2010; 4:1747-1753.
- Jaffery G, Anwar SM, Hussain W, Maqbool S. Serological diagnosis of typhoid fever in children: a comparative evaluation of Salmonella typhi O-9 antigen based rapid essay. 2005.
- Buigut JA. Evaluation of widal tube dilution and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosing typhoid fever at a referral hospital in Kenya. Moi University. 2015.
- Choo K, Davis T, Ismail A, Ibrahim TT, Ghazali W. Rapid and reliable serological diagnosis of enteric fever: comparative sensitivity and specificity of typhidot and typhidot-M tests in febrile Malaysian children. Acta Trop. 1999; 72:175-183. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10206117
- Jesudason M, Esther E, Mathai E. typhidot test to detect IgG & IgM antibodies in typhoid fever. Indian J Med Res. 2002; 116: 70-72. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12592993
- Olsen SJ, Pruckler J, Bibb W, Thanh NTM, Trinh TM, et al. Evaluation of rapid diagnostic tests for typhoid fever. J Clini Microbiol. 2004; 42:1885-1889. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15131144
- Sherwal B, Dhamija R, Randhawa V, Jais M, Kaintura A, et al. A comparative study of typhidot M and widal test in patients of Typhoid fever. J Indian Academy Clini Med. 2004; 5.
- Yadav K, Yadav SK, Parihar G. A comparative study of typhidot and Widal test for rapid diagnosis of Typhoid fever. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2015; 4: 34-38.
Figures:
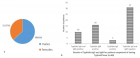
Figure 1
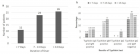
Figure 2
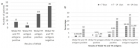
Figure 3
Similar Articles
-
Molecular analysis of immunoglobulins related to Salmonella typhi in pediatric patientsFarah Qudsia, Muhammad Rehan,Samreen Riaz*. Molecular analysis of immunoglobulins related to Salmonella typhi in pediatric patients. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001017; 4: 005-010
Recently Viewed
-
Non-surgical Treatment of Verrucous Hyperplasia on Amputation Stump: A Case Report and Literature ReviewSajeda Alnabelsi*, Reem Hasan, Hussein Abdallah, Suzan Qattini. Non-surgical Treatment of Verrucous Hyperplasia on Amputation Stump: A Case Report and Literature Review. Ann Dermatol Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.adr.1001034; 8: 015-017
-
Outpatient operative hysteroscopy: evaluation of patient satisfaction and acceptanceClare Margaret Crowley*,Noelle Gill,Minna Geisler. Outpatient operative hysteroscopy: evaluation of patient satisfaction and acceptance. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001098; 5: 005-008
-
Predictors of positive treatment response to PTNS in women with overactive bladderSuneetha Rachaneni*,Doyo Enki,Megan Welstand,Thomasin Heggie,Anupreet Dua. Predictors of positive treatment response to PTNS in women with overactive bladder. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001097; 5: 001-004
-
Prediction of neonatal and maternal index based on development and population indicators: a global ecological studySedigheh Abdollahpour,Hamid Heidarian Miri,Talat Khadivzadeh*. Prediction of neonatal and maternal index based on development and population indicators: a global ecological study. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001096; 4: 101-105
-
A Genetic study in assisted reproduction and the risk of congenital anomaliesKaparelioti Chrysoula,Koniari Eleni*,Efthymiou Vasiliki,Loutradis Dimitrios,Chrousos George,Fryssira Eleni. A Genetic study in assisted reproduction and the risk of congenital anomalies. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001095; 4: 096-100
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."