Abstract
Research Article
Uterine precursor lesions in patients with incidental nodal lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A report of 4 cases
Charles M Lombard*
Published: 14 December, 2020 | Volume 4 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-004.
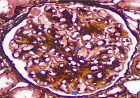
Uterine sections from 6 patients with incidental nodal lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) were examined for LAM lesions by screening these sections with cathepsin K immunohistochemistry (IHC) stains. The hysterectomy specimens were all concurrent with the lymph node dissections in which the nodal LAM was discovered. In 4 of 6 patients microscopic lesions of pre-LAM were identified and confirmed by IHC staining for HMB-45 and beta-catenin. All lesions were grossly inapparent and also inapparent by routine hematoxylin and eosin stains. Three variants of pre-LAM lesions were identified. None of the pre-LAM lesions had an associated lymphatic proliferation. It is proposed that these pre-LAM lesions gave rise to the incidental nodal LAM lesions. Furthermore, it is suggested that the absence of an associated lymphatic proliferation associated with these lesions may be a factor in the attenuated potential for spread and the only rare association of these nodal lesions with pulmonary LAM.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001016 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Nodal lymphangioleiomyomatosis; Uterine precursor lesion; Pathogenesis; Pathology
References
- Schoolmeester JK, Park KJ. Incidental nodal lymphangioleiomyomatosis is not a harbinger of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a study of 19 cases with evaluation of diagnostic immunohistochemistry. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015; 39: 1404-1410. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26135558
- Rabban JT, Firetag B, Sangoi AR, Post MD, Zaloudek CJ. Incidental pelvic and para-aortic lymph node lymphangioleiomyomatosis detected during surgical staging of pelvic cancer in women without symptomatic pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis or tuberous sclerosis complex. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015; 39: 1015-1025. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25786086
- Kuno I, Yoshida J, Shimizu H, Uehara T, Uno M, et al. Incidental lymphangioleiomyomatosis in the lymph nodes of gynecologic surgical specimens. Eur J Ob Gynec Reprod Biol. 2018; 231: 93-97. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30336310
- Hayashi T, Kumasaka T, Mitani K, Terao Y, Watanabe M, et al. Prevalence of uterine and adnexal involvement in pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a clinicopathologic study of 10 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011; 35: 1776-1785. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22020043
- Lombard CM. Microscopic precursor lesions of uterine lymphangioleiomyomatosis associated with incidental nodal lymphangioleiomyomatosis. A case report and discussion of pathogenesis. Hum Pathol Case Rep (in press).
- Flavin RJ, Cook J, Fiorentino M, Bailey D, Brown M, et al. Beta-Catenin is a useful adjunct immunohistochemical marker for the diagnosis of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011; 135: 776-782. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21502434
- Kumasaka T, Seyama K, Mitani K, Sato T, Souma Sm et al. Lymphangiogenesis in lymphangioleiomyomatosis: its implication in the progression of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004; 28: 1007-1016. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15252306
- Gyure KA, Hart WR, Kennedy AW. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis of the uterus associated with tuberous sclerosis and malignant neoplasia of the female genital tract: a report of two cases. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1995; 14: 344-351. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8598338v
Figures:
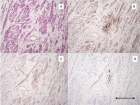
Figure 1
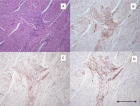
Figure 2
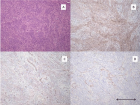
Figure 3
Similar Articles
-
MicroRNA Therapeutics in Triple Negative Breast CancerSarmistha Mitra*. MicroRNA Therapeutics in Triple Negative Breast Cancer . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hjpcr.1001003; 1: 009-017
-
Amyotropyc Lateral Sclerosis and Endogenous -Esogenous Toxicological Movens: New model to verify other Pharmacological StrategiesMauro Luisetto*,Behzad Nili-Ahmadabadi,Nilesh M Meghani,Ghulam Rasool Mashori,Ram Kumar Sahu,Kausar Rehman Khan, Ahmed Yesvi Rafa,Luca Cabianca,Gamal Abdul Hamid, Farhan Ahmad Khan. Amyotropyc Lateral Sclerosis and Endogenous -Esogenous Toxicological Movens: New model to verify other Pharmacological Strategies. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001009; 2: 029-048
-
Receptor pharmacology and other relevant factors in lower urinary tract pathology under a functional and toxicological approach: Instrument to better manage antimicrobials therapyMauro Luisetto*,Naseer Almukhtar,Behzad Nili-Ahmadabadi,Ghulam Rasool Mashori,Kausar Rehman Khan,Ram Kumar Sahu,Farhan Ahmad Khan,Gamal Abdul Hamid,Luca Cabianca. Receptor pharmacology and other relevant factors in lower urinary tract pathology under a functional and toxicological approach: Instrument to better manage antimicrobials therapy . . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001010; 2: 049-093
-
Uterine precursor lesions in patients with incidental nodal lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A report of 4 casesCharles M Lombard*. Uterine precursor lesions in patients with incidental nodal lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A report of 4 cases . . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001016; 4: 001-004.
-
The pathogenesis of psoriasis: insight into a complex “Mobius Loop” regulation processYuankuan Jiang,Haiyang Chen,Jiayue Liu,Tianfu Wei,Peng Ge,Jialin Qu*,Jingrong Lin. The pathogenesis of psoriasis: insight into a complex “Mobius Loop” regulation process. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001024; 5: 020-025
-
Immune-mediated neuropathy related to bortezomib in a patient with multiple myelomaSusanne Koeppen*,Jörg Hense,Kay Wilhelm Nolte,Joachim Weis. Immune-mediated neuropathy related to bortezomib in a patient with multiple myeloma. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001028; 6: 001-004
-
Post-operative agranulocytosis caused by intravenous cefazolin: A case report with a discussion of the pathogenesisCharles M Lombard*,Jiali Li,Bijayee Shrestha. Post-operative agranulocytosis caused by intravenous cefazolin: A case report with a discussion of the pathogenesis. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001030; 6: 009-012
-
Harmonizing Artificial Intelligence Governance; A Model for Regulating a High-risk Categories and Applications in Clinical Pathology: The Evidence and some ConcernsMaxwell Omabe*. Harmonizing Artificial Intelligence Governance; A Model for Regulating a High-risk Categories and Applications in Clinical Pathology: The Evidence and some Concerns. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001040; 8: 001-005
-
The Accuracy of pHH3 in Meningioma Grading: A Single Institution StudyMansouri Nada1, Yaiche Rahma*, Takout Khouloud, Gargouri Faten, Tlili Karima, Rachdi Mohamed Amine, Ammar Hichem, Yedeas Dahmani, Radhouane Khaled, Chkili Ridha, Msakni Issam, Laabidi Besma. The Accuracy of pHH3 in Meningioma Grading: A Single Institution Study. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001041; 8: 006-011
Recently Viewed
-
Cystoid Macular Oedema Secondary to Bimatoprost in a Patient with Primary Open Angle GlaucomaKonstantinos Kyratzoglou*,Katie Morton. Cystoid Macular Oedema Secondary to Bimatoprost in a Patient with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Int J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijceo.1001059; 9: 001-003
-
Navigating Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Current and Emerging Therapies for Neurodegenerative DisordersShashikant Kharat*, Sanjana Mali*, Gayatri Korade, Rakhi Gaykar. Navigating Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Current and Emerging Therapies for Neurodegenerative Disorders. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001095; 8: 033-046
-
Obesity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Separate Clinical PhenotypeDaria A Prokonich*, Tatiana V Saprina, Ekaterina B Bukreeva. Obesity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Separate Clinical Phenotype. J Pulmonol Respir Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001060; 8: 053-055
-
Current Practices for Severe Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Associated COPD and EmphysemaMJ Nicholson*, M Seigo. Current Practices for Severe Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Associated COPD and Emphysema. J Pulmonol Respir Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001058; 8: 044-047
-
Clinical and Histopathological Mismatch: A Case Report of Acral FibromyxomaMonica Mishra*,Kailas Mulsange,Gunvanti Rathod,Deepthi Konda. Clinical and Histopathological Mismatch: A Case Report of Acral Fibromyxoma. Arch Pathol Clin Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001045; 9: 005-007
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."